Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function in the body. There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
- Epithelial tissue: Epithelial tissue is composed of cells that are tightly packed together and form a continuous sheet. This type of tissue covers the surfaces of the body, including the skin, and lines the inner surfaces of organs and cavities. Epithelial tissue functions to protect the body from injury and infection, regulate the exchange of substances between the body and the environment, and secrete and absorb substances.
- Connective tissue: Connective tissue is composed of cells and extracellular matrix, which is a non-cellular material that provides structural support and acts as a medium for the exchange of substances. Connective tissue includes several types of tissues, such as bone, cartilage, blood, and adipose tissue. Connective tissue functions to provide support and protection, store energy, transport substances, and participate in the immune response.
- Muscle tissue: Muscle tissue is composed of cells that are specialized for contraction. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for voluntary movement. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs and is responsible for involuntary movement.
- Nervous tissue: Nervous tissue is composed of cells called neurons and supporting cells called glial cells. Neurons transmit electrical and chemical signals, while glial cells support and protect neurons. Nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, and functions to transmit and process information, control bodily functions, and coordinate responses to stimuli.
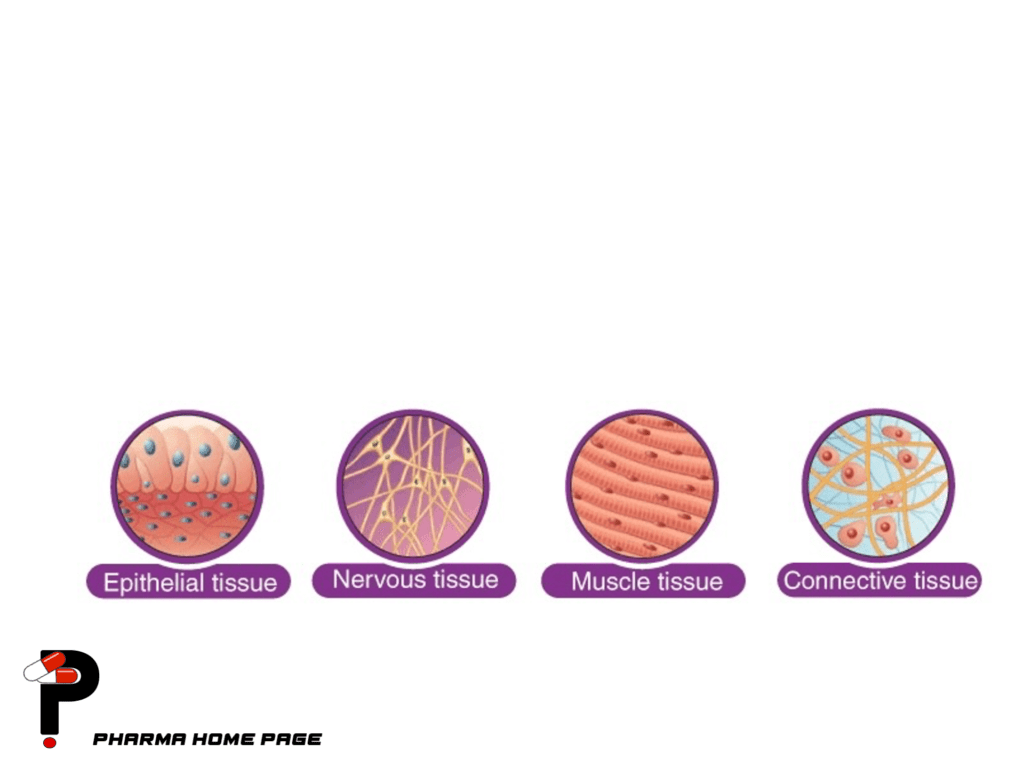
In summary, the main types of tissues, their structure, location, and functions are as follows:
- Epithelial tissue: composed of tightly packed cells forming a continuous sheet; located on surfaces of the body and lining internal organs and cavities; functions to protect, regulate exchange, and secrete/absorb substances.
- Connective tissue: composed of cells and extracellular matrix; includes bone, cartilage, blood, and adipose tissue; functions to provide support, store energy, transport substances, and participate in the immune response.
- Muscle tissue: composed of cells specialized for contraction; includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle; functions to produce movement and generate force.
- Nervous tissue: composed of neurons and glial cells; located in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves; functions to transmit and process information, control bodily functions, and coordinate responses to stimuli.
