Extracellular signaling molecules can activate intracellular signaling pathways by binding to specific receptors on the cell surface. The binding of the signaling molecule to the receptor triggers a series of events, collectively known as signal transduction, that ultimately lead to changes in the activity or behavior of the cell. The process of signal transduction typically involves several steps:
- Receptor activation: The extracellular signaling molecule binds to the receptor on the cell surface, causing a conformational change in the receptor that activates it.
- Second messenger production: The activated receptor then triggers the production of second messengers, such as cyclic AMP (cAMP) or inositol triphosphate (IP3), which transmit the signal from the cell surface to the intracellular environment.
- Activation of protein kinases: The second messengers then activate protein kinases, enzymes that add a phosphate group to other proteins, leading to changes in their activity.
- Activation of transcription factors: The activated protein kinases then activate transcription factors, which are proteins that bind to DNA and regulate gene expression.
- Gene expression changes: The activation of transcription factors ultimately leads to changes in gene expression, resulting in changes in the activity or behavior of the cell.
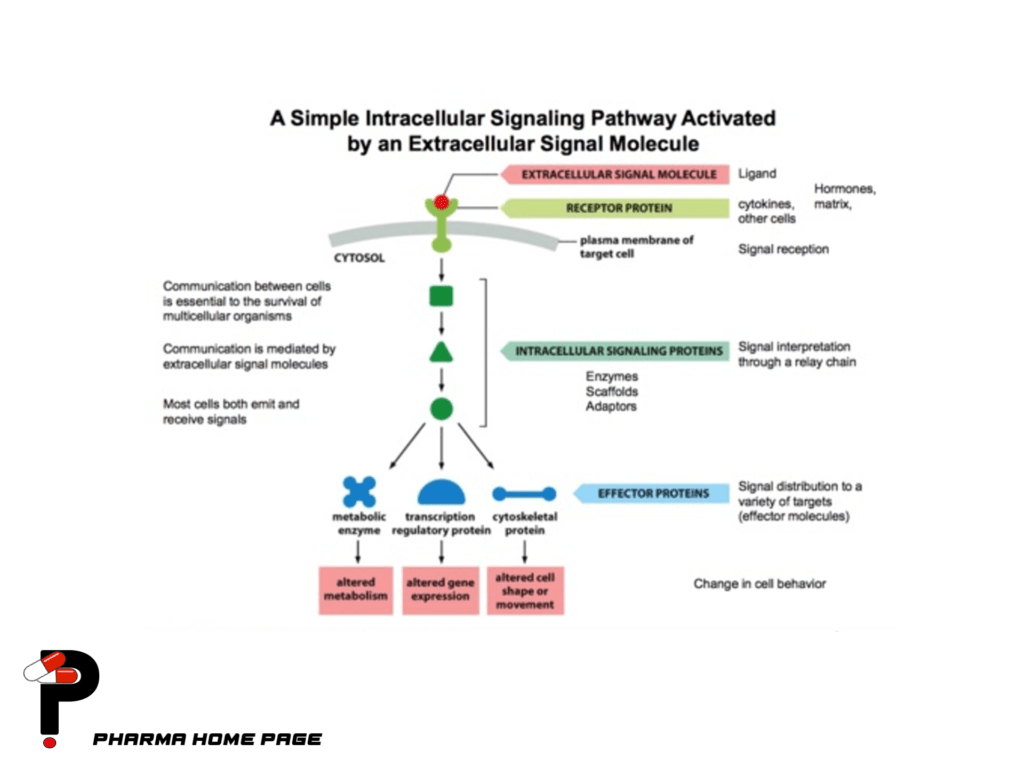
Different extracellular signaling molecules can activate different intracellular signaling pathways, resulting in diverse cellular responses. For example, the signaling molecule insulin activates a signaling pathway that promotes glucose uptake and storage in muscle and fat cells, while the signaling molecule epinephrine activates a signaling pathway that stimulates the breakdown of stored glucose in liver cells.
The activation of intracellular signaling pathways by extracellular signaling molecules plays a critical role in many physiological processes, including growth, development, metabolism, and immune response. Disruptions in these pathways can lead to a variety of diseases and disorders, including cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases. Therefore, the study of intracellular signaling pathways is an important area of research in cell biology and has led to the development of new drugs and therapies for the treatment of many diseases.

Pingback: Forms of intracellular signaling: a) Contact-dependent b) Paracrine c) Synaptic d) Endocrine – PharmaHomePage